
File:Topography Ireland.jpg
| |
This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below.
Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help. |
Summary
|
Warning |
Some browsers may have trouble displaying this image at full resolution: This image has a large number of pixels and may either not load properly or cause your browser to freeze. | Interactive large-image-viewer ( non-Flash) |
|---|
| Description |
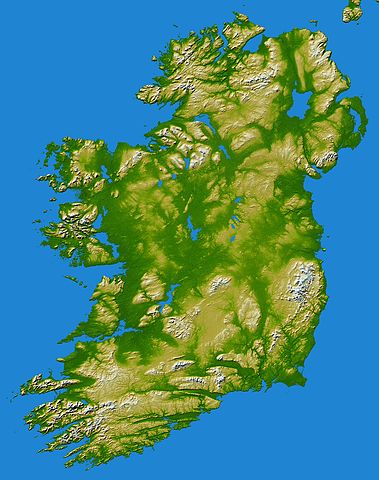
English: Elevation data in this topographical image of Ireland were acquired by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission on board the STS-99 flight of the Space Shuttle Endeavour, launched on 11 February 2000.
The island of Ireland comprises a large central lowland of limestone with a relief of hills surrounded by a discontinuous border of coastal mountains which vary greatly in geological structure. The mountain ridges of the south are composed of old red sandstone separated by limestone river valleys. Granite predominates in the mountains of Counties Galway, Mayo, and Donegal in the west and north-west and in Counties Down and Wicklow on the east coast, while a basalt plateau covers much of the north-east of the country. The central plain, which is broken in places by low hills, is extensively covered with glacial deposits of clay and sand. It has considerable areas of bog and numerous lakes. The island has seen at least two general glaciations and everywhere ice-smoothed rock, mountain lakes, glacial valleys and deposits of glacial sand, gravel and clay mark the passage of the ice. Two visualisation methods were combined to produce this image: shading and colour coding of topographic height. The shade image was derived by computing topographic slope in the northwest-southeast direction, so that northwest slopes appear bright and southeast slopes appear dark. Colour coding is directly related to topographic height, with green at the lower elevations, rising through yellow and tan, to white at the highest elevations. Elevation data used in this image were acquired by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission on board the Space Shuttle Endeavour, launched on 11 February 2000. SRTM used the same radar instrument that comprised the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) that flew twice on the Space Shuttle Endeavour in 1994. SRTM was designed to collect 3-D measurements of the Earth's surface. To collect the 3-D data, engineers added a 60-metre (approximately 200-foot) mast, installed additional C-band and X-band antennas, and improved tracking and navigation devices. The mission was a cooperative project between NASA, the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) of the U.S. Department of Defense and the German and Italian space agencies. It was managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, for NASA's Earth Science Enterprise, Washington, D.C. Location: 53.5 degrees North latitude, 8 degrees West longitude |
| Date | February 2000 |
| Source | NASA (PIA06672) |
| Author | NASA/JPL/NGA |
| This image or video was catalogued by Jet Propulsion Lab of the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) under Photo ID: PIA06672. This tag does not indicate the copyright status of the attached work. A normal copyright tag is still required. See Commons:Licensing for more information. |
Licensing
| Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
 |
This file is in the public domain because it was solely created by NASA. NASA copyright policy states that "NASA material is not protected by copyright unless noted". (See Template:PD-USGov, NASA copyright policy page or JPL Image Use Policy.) |
 |
 |
Warnings:
|
File usage
I want to learn more...
Schools Wikipedia has been carefully checked to give you the best learning experience. SOS Childrens Villages helps more than 2 million people across 133 countries around the world. Why not try to learn more about child sponsorship?
