
BlackBerry
About this schools Wikipedia selection
SOS Children, which runs nearly 200 sos schools in the developing world, organised this selection. See http://www.soschildren.org/sponsor-a-child to find out about child sponsorship.
 |
|
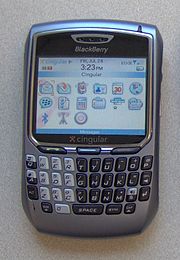
| Compatible networks | GSM850/900/1800/1900 GPRS/ EDGE/ UMTS CDMA/ 1xEV-DO |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 50 mm×106.7 mm×14.5 mm |
| Weight | 87.9 g |
| Memory | 64 MB |
| Display | 320x240 pixels (8300/8700/8800 Series') 240×260 pixels (7100/8100 Series') 65,000 colors |
| Connectivity | microSD, USB, Bluetooth |
The BlackBerry is a wireless handheld device introduced in 1999 which supports push e-mail, mobile telephone, text messaging, internet faxing, web browsing and other wireless information services. Developed by the Canadian company Research In Motion (RIM), it delivers information over the wireless data networks of mobile phone service companies. BlackBerry first made headway in the marketplace by concentrating on e-mail. RIM currently offers BlackBerry e-mail service to non-BlackBerry devices, such as the Palm Treo, through the BlackBerry Connect software. The original BlackBerry device had a monochrome display, but all current models have colour displays.
While including the usual PDA applications (address book, calendar, to-do lists, etc.) as well as telephone capabilities on newer models, the BlackBerry is primarily known for its ability to send and receive e-mail wherever it can access an wireless network of certain cellular phone carriers. It has a built-in keyboard, optimized for " thumbing", the use of only the thumbs to type. System navigation is primarily accomplished by the trackwheel (or "thumbwheel"), a scrolling wheel with a "CLICK" function, located on the right side of the device. Newer models are now utilizing a trackball in the middle of the device as Research In Motion has moved from the trackwheel to the trackball. Some models (currently, those manufactured for use with Nextel, TELUS, and other iDEN networks) also incorporate a two-way radio. Some BlackBerry devices don't depend on mobile phone service coverage and are Wi-Fi compatible like similar handheld devices that are on the marketplace.
Modern BlackBerry handhelds incorporate an ARM 7 or 9 processor, while older BlackBerry 950 and 957 handhelds used Intel 80386 processors. The latest GSM BlackBerry models (8100 and 8700 series) have an Intel PXA901 312 MHz processor, 64 MB flash memory and 16 MB SDRAM. CDMA BlackBerries are based on Qualcomm MSM6x00 chipsets which also include the ARM 9-based processor and GSM 900/1800 roaming(as the case with the 8830). The devices are very popular with some businesses, where they are primarily used to provide e-mail access to roaming employees. To fully integrate the BlackBerry into a company's systems, the installation of BlackBerry Enterprise Server (BES) is required.
On April 11 2007, RIM announced the number of BlackBerry subscribers had reached 8 million.
Keyboard
Most BlackBerry devices come with a full, albeit tiny, QWERTY keyboard, using the "Alt" key to enter numbers and special characters. A self-configurable "AutoText" feature can be used for frequent words or easier input of special characters like umlauts, The 7100 series and Pearl (8100) devices feature a reduced-key keyboard and use a technology called 'SureType.' SureType allows each key to represent multiple letters, numbers, and symbols and uses a prediction dictionary to figure out which word a user will want, similar to Tegic's T9, used on many cellphones.
Operating system
RIM provides a proprietary multi-tasking operating system (OS) for the BlackBerry, which makes heavy use of the device's specialized input devices, particularly the thumbwheel. The OS provides support for MIDP 1.0 and WAP 1.2. Previous versions allowed wireless synchronization with Microsoft Exchange Server's e-mail and calendar, as well as with Lotus Domino's e-mail. The current OS 4 provides a subset of MIDP 2.0, and allows complete wireless activation and synchronization with Exchange's e-mail, calendar, tasks, notes and contacts, and adds support for Novell GroupWise and Lotus Notes.
Third-party developers can write software using these APIs, and proprietary BlackBerry APIs as well, but any application that makes use of certain restricted functionality must be digitally signed so that it can be associated to a developer account at RIM. This signing procedure guarantees the authorship of an application, but does not guarantee the quality or security of the code.
CPU
Early BlackBerry CPUs were Intel 80386 based. Later BlackBerrys, such as the 8700, and the Pearl, are ARM XScale ARMv5TE PXA900 based.
Database
Data extracted from a BlackBerry to a host computer is stored in a single file in IPD format.
Supporting software
BlackBerry handheld integration into an organization's e-mail system is provided through a software package called " BlackBerry Enterprise Server" (BES). Versions of BES are available for Microsoft Exchange, Lotus Domino and Novell GroupWise.
Individual users can often use e-mail services provided by the wireless provider and therefore may not be required to install a BES server on their local network, but organizations that have multiple wireless users usually run BES on their own network. While it can be very expensive owning a BES, third party companies provide hosted BES solutions. These are solutions with most of the advantages of a private BES, but without the costs. Every BlackBerry has a unique id called BlackBerry PIN which is used to identify your device to the BES.
BES can act as a sort of e-mail relay for corporate accounts so that users always have access to their e-mail. The software monitors the user's local "inbox", and when a new message comes in, it picks up the message and passes it to RIM's Network Operations Centre (NOC). The messages are then relayed to the user's wireless provider, which in turn delivers them to the user's BlackBerry device. This is called Push procedure, where the mobile user doesn't have to synchronize the data by hand. All new e-mails, contacts and calendar entries are pushed to the BlackBerry device automatically. Device storage also enables the mobile user to access all data offline in areas without wireless service. As soon as the user connects again, the BES sends the latest data. This way the handheld is always up-to-date.
BES also provides handhelds with TCP/IP connectivity that is proxied through a component called " Mobile Data Service" (MDS). This allows for custom application development using data streams on BlackBerry devices based on the Sun Microsystems Java ME platform.
In addition, BES provides security, in the form of Triple DES or, more recently, AES encryption of all data (both e-mail and MDS traffic) that travels between the BlackBerry handheld and a BlackBerry Enterprise Server.
The universal and push-based connectivity of the BES/MDS infrastructure are among the most valuable aspects of Research In Motion's product. An organization can have devices on different carriers, and connected through different cellular network protocols, all functioning in an integrated fashion.
Most providers offer flat monthly pricing for unlimited data between BlackBerry units and BES, which also enhances the value of the component. In addition to receiving e-mail, organizations can make intranets or custom internal applications with unmetered traffic.
With more recent versions of the BlackBerry platform, the MDS is no longer a requirement for wireless data access. Beginning with OS 3.8 or 4.0, BlackBerry handhelds can access the Internet (i.e. TCP/IP access) without an MDS - previously only e-mail and WAP access was possible without a BES/MDS. The BES/MDS is still required for secure e-mail, data access, and applications that require WAP from carriers that do not allow WAP access.
Criticism
RIM have been criticized for not including 3G/UMTS on any models other than the 8700 series. However, email delivery on 3G units is often slower than EDGE and even GPRS, as emails are broken down into very small packets, each with its own encryption key. The UMTS networks are more suited to streaming media, so for BES/BIS email delivery there is little or no advantage.. On the other hand, new multimedia features--like the ability to email large attachments such as cameraphone photos, as well as the ability to tether BlackBerry as a modem for laptop--provide a compelling reason to add 3G support to future BlackBerries, provided they can keep EDGE support for times when 3G is not favourable.
A major reason for there being no initial support of 3G (UMTS/HSPA) by RIM is the requirement for high power consumption by devices operating on 3G networks. RIM is an industry leader when it comes to battery life and although there are 3G BlackBerry devices coming in 2008, allowing for extra time to bring them to market was reportedly to ensure new devices perform well from a power consumption/battery performance perspective.
In addition, BlackBerrys do not have a touchscreen. This is one area in which some Windows Mobile devices differ, as some Phone Edition devices have a touchscreen. However, users may find the BlackBerry interface simpler as there are generally fewer options available during operation.
Name origin
RIM settled on the name "BlackBerry" only after weeks of work by Lexicon Branding Inc., the Sausalito, California-based firm that named Intel Corp.’s Pentium microprocessor and Apple’s PowerBook. One of the naming experts at Lexicon thought the miniature buttons on RIM’s product looked "like the tiny seeds in a strawberry," Lexicon founder David Placek says. "A linguist at the firm thought straw was too slow sounding. Someone else suggested blackberry. RIM went for it." Previously the device was called LeapFrog, alluding to the technology leaping over the current competition.
Nicknames
The ability to read e-mail that is received in realtime, anywhere, has made the BlackBerry devices infamously addictive, earning them the nickname "CrackBerry". Use of the term CrackBerry became so wide spread that in November 2006 Webster's New World College Dictionary named "crackberry" the "New Word of the Year".
Within the company, various model families are named after subatomic particles; names used include Tachyon (BlackBerry 5810), Tachyon 2 (BlackBerry 6700), Electron, Proton, Baryon, Quark (BlackBerry 7200) and Charm.
Models
- Early Pager Models: 850, 857, 950, 957
- Monochrome Java-based Models: 5000-series and 6000-series
- First Colour Models: 7200-series, 7500-series and 7700-series
- First SureType Phone Models: 7100-series
- Modern BlackBerry Models: 8000-series including BlackBerry Pearl and BlackBerry Curve
Phones with BlackBerry e-mail client
Several ordinary mobile phones have been released featuring the BlackBerry e-mail client which connects to BlackBerry servers. All these phones have full QWERTY keyboards (except the Motorola MPx220, Nokia E50, Nokia E60, and Samsung t719).
- HTC Advantage X7500
- HTC TyTN Operates on 3G/HSDPA/850/900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 240x320 pixel touch screen, QWERTY keyboard
- Motorola MPx220 (selected models only), Operates on 850/900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 176x220 pixel screen
- Nokia 6810 Operates on 900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 128x128 pixel screen
- Nokia 6820 Operates on 900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, American variant on 850/1800/1900 GSM network, 128x128 pixel screen
- Nokia 9300 Operates on 900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 128x128 and 640x200 pixel screen
- Nokia 9300i Operates on 900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 128x128 and 640x200 pixel screen
- Nokia 9500 Operates on 900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 128x128 and 640x200 pixel screen
- Nokia E50 Operates on 850/900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 320x240 pixel screen
- Nokia E51 Operates on 3G-UMTS/HSDPA 850/900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 240x320 pixel screen
- Nokia E60 Operates on 850/900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 416x352 pixel screen
- Nokia E61 Operates on 3G-UMTS/850/900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 320x240 pixel screen
- Nokia E61i Operates on 3G-UMTS/850/900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 320x240 pixel screen
- Nokia E62 Operates on 850/900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 320x240 pixel screen
- Nokia E70 Operates on 850/900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 416x352 pixel screen
- Nokia E90
- Qtek 9100 Operates on 850/900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 240x320 pixel touch screen and QWERTY keyboard
- Qtek 9000 Operates on 3G-UMTS/850/900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 640x480 pixel touch screen, QWERTY keyboard
- Samsung t719 Operates on 850/900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 176x220 pixel screen
- Siemens SK65, Operates on 900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, 132x176 pixel screen
- Sony Ericsson P910 Operates on 900/1800/1900 MHz GSM network, American and Chinese variants on 850/1800/1900, 208x320 pixel screen
- Sony Ericsson P990
- Sony Ericsson M600i
- Sony Ericsson P1
Certification
- BCESA (Blackberry Certified Enterprise Sales Associate, BCESA40 in full) is a Blackberry Certification for professional users of RIM ( Research In Motion) Blackberry wireless e-mail devices.
The Certification requires the user to pass several exams relating to the Blackberry Device, all its functions including Desktop software and providing technical support to Customers of Blackberry Devices.
The BCESA, Blackberry Certified Enterprise Sales Associate qualification, is the first of three levels of professional Blackberry Certification.
- BCTA (BlackBerry Certified Technical Associate)
- BlackBerry Certified Support Associate T2
Additional information on certifications can be found here.

