Geography of Guinea
Did you know...
Arranging a Wikipedia selection for schools in the developing world without internet was an initiative by SOS Children. To compare sponsorship charities this is the best sponsorship link.
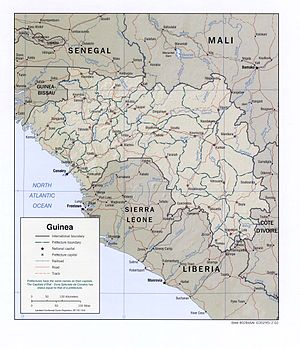
Guinea Coast of West Africa and is bordered by Guinea-Bissau, Senegal, Mali, Côte d'Ivoire, Liberia, and Sierra Leone. The country is divided into four geographic regions: A lowland belt running north to south behind the coast ( Lower Guinea), which is part of the Guinean forest-savanna mosaic ecoregion; the pastoral Fouta Djallon highlands ( Middle Guinea); the northern savanna ( Upper Guinea); and a southeastern rain-forest region ( Forest Guinea). The Niger, Gambia, and Senegal Rivers are among the 22 West African rivers that have their origins in Guinea.
Climate
The coastal region of Guinea and most of the inland have a tropical climate, with a rainy season lasting from April to November, relatively high and uniform temperatures, and high humidity. Conakry's year-round average high is 29 °C (84.2 °F), and the low is 23 °C (73.4 °F); its average annual rainfall is 4,300 mm (169.3 in). Sahelian Upper Guinea has a shorter rainy season and greater daily temperature variations.
General information
Location: Western Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Guinea-Bissau and Sierra Leone
Geographic coordinates: 11°00′N 10°00′W
Map references: Africa
Area:
total: 245,857 km²
land: 245,857 km²
water: 0 km²
Area - comparative: slightly smaller than Oregon
Land boundaries:
- total:
3,399 km
- border countries:
Côte d'Ivoire 610 km, Guinea-Bissau 386 km, Liberia 563 km, Mali 858 km, Senegal 330 km, Sierra Leone 652 km
Coastline: 320 km
Maritime claims:
exclusive economic zone: 200 nmi (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
Climate: generally hot and humid; monsoonal-type rainy season (June to November) with southwesterly winds; dry season (December to May) with northeasterly harmattan winds
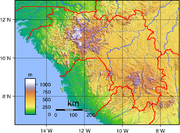
Terrain: generally flat coastal plain, hilly to mountainous interior
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point: Mont Nimba 1,752 m
Natural resources: bauxite, iron ore, diamonds, gold, uranium, hydropower, fish
Land use:
arable land: 2%
permanent crops: 0%
permanent pastures: 22%
forests and woodland: 59%
other: 17% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 930 km² (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: hot, dry, dusty harmattan haze may reduce visibility during dry season
Environment - current issues: deforestation; inadequate supplies of potable water; desertification; soil contamination and erosion; overfishing, overpopulation in forest region
Environment - international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements