
England in the Middle Ages
Background Information
SOS Children made this Wikipedia selection alongside other schools resources. A good way to help other children is by sponsoring a child
Great Britain during the Middle Ages (from the 5th century withdrawal of Roman forces from the province of Britannia and the Germanic invasions, until the Early modern period) was fragmented into a number of independent kingdoms. By the High Middle Ages, after the end of the Viking Age and the Norman Conquest, the kingdoms of England and Scotland emerge as the main poles of political power.
The medieval period in England can be dated from the arrival in Kent of Anglo-Saxon troops led by the legendary Hengest and Horsa. Subsequently the Brythonic, Celtic powers were conquered by Jutes, Angles and Saxons Germanic tribes, from the contemporary Angeln and Jutland areas of northern Germany and mainland Denmark. Political takeover of other areas of England proceeded piecemeal and was not completed until the tenth century.
Similarly, the end of the medieval period is usually dated by the rise of what is often referred to as the " English Renaissance" in the reign of Henry VIII of England, and the Reformation in Scotland, or else to the establishment of a centralized, bureaucratic monarchy by Henry VII of England. From a political point of view, the Norman Conquest of England divides medieval Britain in two distinct phases of cultural and political history. From a linguistic point of view the Norman Conquest had only a limited effect, Old English evolving into Middle English, although the Anglo Norman language would remain the language of those that ruled for two centuries at least, before mingling with Middle English.
At the height of pre-Norman medieval English power, a single English king ruled from the border with Scotland to the border with Wales to the border with Cornwall. After the Norman Conquest, English power intruded into Wales with increasing vigour, but the process of consolidation was continuous and is not just a medieval feature. The other problem with suggesting such a unity is that the various states had relations with Scandinavia and Continental Europe which are excluded by the concept. For example, northern Scotland often had closer ties with Norway and France (see Auld Alliance) than England or Wales in the medieval period, with Orkney and Shetland only becoming part of Scotland in 1471. Southern England, due to its proximity to Normandy, Flanders and Brittany, had closer relations with them than the other regions.
Periodisation
- Sub-Roman Britain (5th to 6th centuries)
- Early Middle Ages (7th to 11th centuries): England, Scotland, Wales
- Anglo-Saxon England
- Viking Age
- High Middle Ages (11th to 15th centuries): England, Scotland, Wales
- Norman rule (1066-1154)
- House of Plantagenet
 ( 1154– 1485)
( 1154– 1485) - House of Dunkeld (1058–1286)
- House of Balliol (1292–1338)
- Late Middle Ages (14th and 15th centuries): England, Scotland, Wales
- Transition to Early Modern Britain
List of states
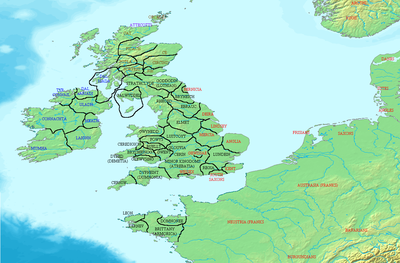
Britain was fragmented into numerous kingdoms during the Early Middle Ages. In the High Middle Ages, the two kingdoms of England ( Athelstan of England, 927) and Scotland or Alba ( Kenneth I of Scotland, 843) gained prominence, merged into the United Kingdom in 1707.
Early Middle Ages
Angle, Saxon and Jute states
See: Heptarchy
Southern Celtic states
- Brycheiniog
- Buellt
- Calchfynydd
- Ceredigion
- Cornwall (Kingdom of Kernow)
- Deheubarth (950-1271)
- Devon
- Dogfeiling
- Dumnonia
- Dunoding
- Dyfed
- Elfael
- Ergyng
- Glywysing
- Gwerthrynion
- Gwynedd (5th c.-1282)
- Gwynllwg
- Gwent
- Llŷn
- Meirionnydd
- Morgannwg
- Pennines
- Pengwern
- Penychen
- Powys
- Rheged
- Rhos
- Seisyllwg
- Senghenydd
- Tegeingl
Northern Celtic; Scottish, Pict and Caledonian states
- Alba
- Argyll
- Caithness
- Cumbria
- Dál Riata
- Dumbarton
- Elmet
- Fortriu
- Galloway
- Gododdin
- Lothian
- Manaw Gododdin
- Mar
- Moray
- Pictavia
- Rheged
- Strathclyde
- Bernicia
Viking Age
- Danelaw
- Earldom of Orkney (867-1468)
- Jórvík (867-954)
- House of Alpin (843–878) & (889–1040)
- House of Moray (1040–1058)
High Middle Ages
post-1066 states
- Norman England (1066-1154)
- House of Plantagenet
 ( 1154– 1485)
( 1154– 1485) - Kingdom of Man (1079-1266)
- Galloway (11th c.-1234)
- House of Dunkeld (1058–1286)
- House of Balliol (1292–1296)

