Religion
About this schools Wikipedia selection
Arranging a Wikipedia selection for schools in the developing world without internet was an initiative by SOS Children. Before you decide about sponsoring a child, why not learn about different sponsorship charities first?
| Religions by country |
|---|
|
Africa
Asia
Europe
Middle East
North America
Oceania
South America
|
Religion is an organized collection of belief systems, cultural systems, and world views that relate humanity to spirituality and, sometimes, to moral values. Many religions have narratives, symbols, traditions and sacred histories that are intended to give meaning to life or to explain the origin of life or the Universe. From their ideas about the cosmos and human nature, they tend to derive morality, ethics, religious laws or a preferred lifestyle. According to some estimates, there are roughly 4,200 religions in the world.
Many religions may have organized behaviors, clergy, a definition of what constitutes adherence or membership, holy places, and scriptures. The practice of a religion may also include rituals, sermons, commemoration or veneration of a deity, gods or goddesses, sacrifices, festivals, feasts, trance, initiations, funerary services, matrimonial services, meditation, prayer, music, art, dance, public service or other aspects of human culture. Religions may also contain mythology.
The word religion is sometimes used interchangeably with faith or belief system; however, in the words of Émile Durkheim, religion differs from private belief in that it is "something eminently social". A global 2012 poll reports that 59% of the world's population is religious, 23% are not religious, and 13% are atheists.
Etymology
Religion (from O.Fr. religion "religious community," from L. religionem (nom. religio) "respect for what is sacred, reverence for the gods," "obligation, the bond between man and the gods") is derived from the Latin religiō, the ultimate origins of which are obscure. One possibility is derivation from a reduplicated *le-ligare, an interpretation traced to Cicero connecting lego "read", i.e. re (again) + lego in the sense of "choose", "go over again" or "consider carefully". Modern scholars such as Tom Harpur and Joseph Campbell favour the derivation from ligare "bind, connect", probably from a prefixed re-ligare, i.e. re (again) + ligare or "to reconnect," which was made prominent by St. Augustine, following the interpretation of Lactantius. The medieval usage alternates with order in designating bonded communities like those of monastic orders: "we hear of the 'religion' of the Golden Fleece, of a knight 'of the religion of Avys'".
According to the philologist Max Müller, the root of the English word "religion", the Latin religio, was originally used to mean only "reverence for God or the gods, careful pondering of divine things, piety" (which Cicero further derived to mean "diligence"). Max Müller characterized many other cultures around the world, including Egypt, Persia, and India, as having a similar power structure at this point in history. What is called ancient religion today, they would have only called "law".
Many languages have words that can be translated as "religion", but they may use them in a very different way, and some have no word for religion at all. For example, the Sanskrit word dharma, sometimes translated as "religion", also means law. Throughout classical South Asia, the study of law consisted of concepts such as penance through piety and ceremonial as well as practical traditions. Medieval Japan at first had a similar union between "imperial law" and universal or "Buddha law", but these later became independent sources of power.
There is no precise equivalent of "religion" in Hebrew, and Judaism does not distinguish clearly between religious, national, racial, or ethnic identities. One of its central concepts is " halakha", sometimes translated as "law"", which guides religious practice and belief and many aspects of daily life.
The use of other terms, such as obedience to God or Islam are likewise grounded in particular histories and vocabularies.
Definitions
There are numerous definitions of religion and only a few are stated here. The typical dictionary definition of religion refers to a "belief in, or the worship of, a god or gods" or the "service and worship of God or the supernatural". However, writers and scholars have expanded upon the "belief in god" definitions as insufficient to capture the diversity of religious thought and experience.
Edward Burnett Tylor defined religion as "the belief in spiritual beings". He argued, back in 1871, that narrowing the definition to mean the belief in a supreme deity or judgment after death or idolatry and so on, would exclude many peoples from the category of religious, and thus "has the fault of identifying religion rather with particular developments than with the deeper motive which underlies them". He also argued that the belief in spiritual beings exists in all known societies.
The anthropologist Clifford Geertz defined religion as a "system of symbols which acts to establish powerful, pervasive, and long-lasting moods and motivations in men by formulating conceptions of a general order of existence and clothing these conceptions with such an aura of factuality that the moods and motivations seem uniquely realistic. Alluding perhaps to Tylor's "deeper motive", Geertz remarked that "we have very little idea of how, in empirical terms, this particular miracle is accomplished. We just know that it is done, annually, weekly, daily, for some people almost hourly; and we have an enormous ethnographic literature to demonstrate it". The theologian Antoine Vergote also emphasized the "cultural reality" of religion, which he defined as "the entirety of the linguistic expressions, emotions and, actions and signs that refer to a supernatural being or supernatural beings"; he took the term "supernatural" simply to mean whatever transcends the powers of nature or human agency.
The sociologist Durkheim, in his seminal book The Elementary Forms of the Religious Life, defined religion as a "unified system of beliefs and practices relative to sacred things". By sacred things he meant things "set apart and forbidden — beliefs and practices which unite into one single moral community called a Church, all those who adhere to them". Sacred things are not, however, limited to gods or spirits. On the contrary, a sacred thing can be "a rock, a tree, a spring, a pebble, a piece of wood, a house, in a word, anything can be sacred". Religious beliefs, myths, dogmas and legends are the representations that express the nature of these sacred things, and the virtues and powers which are attributed to them.
In his book The Varieties of Religious Experience, the psychologist William James defined religion as "the feelings, acts, and experiences of individual men in their solitude, so far as they apprehend themselves to stand in relation to whatever they may consider the divine". By the term "divine" James meant "any object that is godlike, whether it be a concrete deity or not" to which the individual feels impelled to respond with solemnity and gravity.
Echoes of James' and Durkheim's definitions are to be found in the writings of, for example, Frederick Ferré who defined religion as "one's way of valuing most comprehensively and intensively". Similarly, for the theologian Paul Tillich, faith is "the state of being ultimately concerned", which "is itself religion. Religion is the substance, the ground, and the depth of man's spiritual life."
When religion is seen in terms of "sacred", "divine", intensive "valuing", or "ultimate concern", then it is possible to understand why scientific findings and philosophical criticisms (e.g. Richard Dawkins) do not necessarily disturb its adherents.
Origins and development
The origin of religion is uncertain, but it has been suggested that it evolved for the nurture of children. There are a number of theories regarding the subsequent origins of organized religious practices. According to anthropologists John Monaghan and Peter Just, "Many of the great world religions appear to have begun as revitalization movements of some sort, as the vision of a charismatic prophet fires the imaginations of people seeking a more comprehensive answer to their problems than they feel is provided by everyday beliefs. Charismatic individuals have emerged at many times and places in the world. It seems that the key to long-term success – and many movements come and go with little long-term effect – has relatively little to do with the prophets, who appear with surprising regularity, but more to do with the development of a group of supporters who are able to institutionalize the movement."
The development of religion has taken different forms in different cultures. Some religions place an emphasis on belief, while others emphasize practice. Some religions focus on the subjective experience of the religious individual, while others consider the activities of the religious community to be most important. Some religions claim to be universal, believing their laws and cosmology to be binding for everyone, while others are intended to be practiced only by a closely defined or localized group. In many places religion has been associated with public institutions such as education, hospitals, the family, government, and political hierarchies. Anthropologists John Monoghan and Peter Just state that, "it seems apparent that one thing religion or belief helps us do is deal with problems of human life that are significant, persistent, and intolerable. One important way in which religious beliefs accomplish this is by providing a set of ideas about how and why the world is put together that allows people to accommodate anxieties and deal with misfortune."
One modern academic theory of religion, social constructionism, says that religion is a modern concept that suggests all spiritual practice and worship follows a model similar to the Abrahamic religions as an orientation system that helps to interpret reality and define human beings, and thus religion, as a concept, has been applied inappropriately to non-Western cultures that are not based upon such systems, or in which these systems are a substantially simpler construct.
Types of religion
Categories
Some scholars classify religions as either universal religions that seek worldwide acceptance and actively look for new converts, or ethnic religions that are identified with a particular ethnic group and do not seek converts. Others reject the distinction, pointing out that all religious practices, whatever their philosophical origin, are ethnic because they come from a particular culture.
In the 19th and 20th centuries, the academic practice of comparative religion divided religious belief into philosophically defined categories called "world religions." However, some recent scholarship has argued that not all types of religion are necessarily separated by mutually exclusive philosophies, and furthermore that the utility of ascribing a practice to a certain philosophy, or even calling a given practice religious, rather than cultural, political, or social in nature, is limited. The current state of psychological study about the nature of religiousness suggests that it is better to refer to religion as a largely invariant phenomenon that should be distinguished from cultural norms (i.e. "religions").
Some academics studying the subject have divided religions into three broad categories:
- world religions, a term which refers to transcultural, international faiths;
- indigenous religions, which refers to smaller, culture-specific or nation-specific religious groups; and
- new religious movements, which refers to recently developed faiths.
Interfaith cooperation
Because religion continues to be recognized in Western thought as a universal impulse, many religious practitioners have aimed to band together in interfaith dialogue, cooperation, and religious peacebuilding. The first major dialogue was the Parliament of the World's Religions at the 1893 Chicago World's Fair, which remains notable even today both in affirming "universal values" and recognition of the diversity of practices among different cultures. The 20th century has been especially fruitful in use of interfaith dialogue as a means of solving ethnic, political, or even religious conflict, with Christian–Jewish reconciliation representing a complete reverse in the attitudes of many Christian communities towards Jews.
Recent interfaith initiatives include "A Common Word", launched in 2007 and focused on bringing Muslim and Christian leaders together, the "C1 World Dialogue", the "Common Ground" initiative between Islam and Buddhism, and a United Nations sponsored "World Interfaith Harmony Week".
Religious groups
The list of still-active religious movements given here is an attempt to summarize the most important regional and philosophical influences on local communities, but it is by no means a complete description of every religious community, nor does it explain the most important elements of individual religiousness.
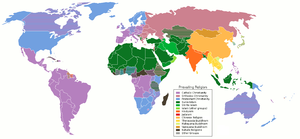
The five largest religious groups by world population, estimated to account for 5 billion people, are Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Hinduism (with the relative numbers for Buddhism and Hinduism dependent on the extent of syncretism) and Chinese folk religion.
| Five largest religions | Adherents in 2000 | % of world population | Demographics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Christianity | 2.0 billion | 33% | Christianity by country |
| Islam | 1.2 billion | 19.6% | Islam by country |
| Hinduism | 811 million | 13.4% | Hinduism by country |
| Chinese folk religion | 385 million | 6.4% | Chinese folk religion |
| Buddhism | 360 million | 5.9% | Buddhism by country |
Abrahamic
Abrahamic religions are monotheistic religions which believe they descend from Abraham.
- Judaism is the oldest Abrahamic religion, originating in the people of ancient Israel and Judea. Judaism is based primarily on the Torah, a text which some Jews believe was handed down to the people of Israel through the prophet Moses. This along with the rest of the Hebrew Bible and the Talmud are the central texts of Judaism. The Jewish people were scattered after the destruction of the Temple in Jerusalem in 70 CE. Today there are about 13 million Jews, about 40 per cent living in Israel and 40 per cent in the United States.
- Christianity is based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth (1st century) as presented in the New Testament. The Christian faith is essentially faith in Jesus as the Christ, the Son of God, and as Savior and Lord. Almost all Christians believe in the Trinity, which teaches the unity of Father, Son (Jesus Christ), and Holy Spirit as three persons in one Godhead. Most Christians can describe their faith with the Nicene Creed. As the religion of Byzantine Empire in the first millennium and of Western Europe during the time of colonization, Christianity has been propagated throughout the world. The main divisions of Christianity are, according to the number of adherents:
- Catholic Church, headed by the Pope in Rome, is a communion of the Western church and 22 Eastern Catholic churches.
- Protestantism, separated from the Catholic Church in the 16th-century Reformation and split in many denominations,
- Eastern Christianity, which include Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy and the Church of the East.
-
- There are other smaller groups, such as Jehovah's Witnesses and the Latter Day Saint movement, whose inclusion in Christianity is sometimes disputed.

- Islam is based on the Quran, one of the holy books considered by Muslims to be revealed by God, and on the teachings of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, a major political and religious figure of the 7th century CE. Islam is the most widely practiced religion of Southeast Asia, North Africa, Western Asia and Central Asia, while Muslim-majority countries also exist in parts of South Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Europe. The two largest sects are Sunni and Shia, although there are other minor groups as well. Wahhabi is the dominant Muslim schools of thought in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. There are also several Islamic republics, including Iran, Pakistan, Mauritania and Afghanistan.
- The Bahá'í Faith is an Abrahamic religion founded in 19th century Iran and since then has spread worldwide. It teaches unity of all religious philosophies and accepts all of the prophets of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam as well as additional prophets including its founder Bahá'u'lláh.
- Smaller regional Abrahamic groups, including Samaritanism (primarily in Israel and the West Bank), the Rastafari movement (primarily in Jamaica), and Druze (primarily in Syria and Lebanon).
Indian
Indian religions are practiced or were founded in the Indian subcontinent. They are sometimes classified as the dharmic religions, as they all feature dharma, a concept of divine duty.
- Hinduism is a synecdoche describing the similar philosophies of Vaishnavism, Shaivism, and related groups practiced or founded in the Indian subcontinent. Concepts most of them share in common include karma, caste, reincarnation, mantras, yantras, and darśana. Hinduism is the most ancient of still-active religions, with origins perhaps as far back as prehistoric times. Hinduism is not a monolithic religion but a religious category containing dozens of separate philosophies amalgamated as Sanātana Dharma, which is the name with whom Hinduism has been known throughout history by its followers.
- Jainism, taught primarily by Parsva (9th century BCE) and Mahavira (6th century BCE), is an ancient Indian religion that prescribes a path of non-violence for all forms of living beings in this world. Jains are found mostly in India.
- Buddhism was founded by Siddhattha Gotama in the 6th century BCE. Buddhists generally agree that Gotama aimed to help sentient beings end their suffering (dukkha) by understanding the true nature of phenomena, thereby escaping the cycle of suffering and rebirth ( saṃsāra), that is, achieving Nirvana.
- Theravada Buddhism, which is practiced mainly in Sri Lanka and Southeast Asia alongside folk religion, shares some characteristics of Indian religions. It is based in a large collection of texts called the Pali Canon.
- Mahayana Buddhism (or the "Great Vehicle") under which are a multitude of doctrines that began their development in China and are still relevant in Vietnam, Korea, Japan and to a lesser extent in Europe and the United States. Mahayana Buddhism includes such disparate teachings as Zen, Pure Land, and Soka Gakkai.
- Vajrayana Buddhism first appeared in India in the 3rd century CE. It is currently most prominent in the Himalaya regions and extends across all of Asia (cf. Mikkyō).
- Two notable new Buddhist sects are Hòa Hảo and the Dalit Buddhist movement, which were developed separately in the 20th century.
- Sikhism is a monotheistic religion founded on the teachings of Guru Nanak and ten successive Sikh Gurus in 15th century Punjab. Sikhs are found mostly in India.
Iranian
Iranian religions are ancient religions whose roots predate the Islamization of Greater Iran. Nowadays these religions are practiced only by minorities.
- Zoroastrianism is a religion and philosophy based on the teachings of prophet Zoroaster in the 6th century BC. The Zoroastrians worship the Creator Ahura Mazda. In Zoroastrianism good and evil have distinct sources, with evil trying to destroy the creation of Mazda, and good trying to sustain it.
- Mandaeism is a monotheistic religion with a strongly dualistic worldview. Mandaeans are sometime labeled as the "Last Gnostics".
- Kurdish religions include the traditional beliefs of the Yazidi, Alevi, and Ahl-e Haqq. Sometimes these are labeled Yazdânism.
Folk
The term folk refers to a broad category of traditional religions that includes shamanism and elements of animism and ancestor worship, where traditional means "indigenous, that which is aboriginal or foundational, handed down from generation to generation…". These are religions that are closely associated with a particular group of people, ethnicity or tribe; they often have no formal creeds or sacred texts. Some faiths are syncretic, fusing diverse religious beliefs and practices.
- Traditional African religions, e.g: Khoisan, Akan, Nupe and Badimo.
- Chinese folk religion, e.g.: Confucianism and Taoism with some remnants of Mahayana Buddhism. New religious movements include Falun Gong and I-Kuan Tao.
- Other folk religions in Asia-Pacific region, e.g.: Cheondoism, Korean shamanism, Shinbutsu-shūgō and Modekngei.
- Australian Aboriginal mythology.
- Folk religions of the Americas, e.g.: Native American religion, Santería, Vodou, Candomblé and Umbanda.
Folk religions are often omitted as a category in surveys even in countries where they are widely practiced, e.g. in China.
New
New religious movements include:
- Shinshūkyō is a general category for a wide variety of religious movements founded in Japan since the 19th century. These movements share almost nothing in common except the place of their founding. The largest religious movements centered in Japan include Soka Gakkai, Tenrikyo, and Seicho-No-Ie among hundreds of smaller groups.
- Cao Đài is a syncretistic, monotheistic religion, established in Vietnam in 1926.
- Raëlism is a new religious movement founded in 1974 teaching that humans were created by aliens. It is numerically the world's largest UFO religion.
- Hindu reform movements, such as Ayyavazhi, Swaminarayan Faith and Ananda Marga, are examples of new religious movements within Indian religions.
- Unitarian Universalism is a religion characterized by support for a "free and responsible search for truth and meaning", and has no accepted creed or theology.
- Noahidism is a Biblical-Talmudic and monotheistic ideology for non-Jews based on the Seven Laws of Noah, and on their traditional interpretations within Judaism.
- Scientology teaches that people are immortal beings who have forgotten their true nature. Its method of spiritual rehabilitation is a type of counseling known as auditing, in which practitioners aim to consciously re-experience painful or traumatic events in their past in order to free themselves of their limiting effects.
- Eckankar is a pantheistic religion with the purpose of making God an everyday reality in one's life.
- Wicca is a neo-pagan religion first popularised in 1954 by British civil servant Gerald Gardner, involving the worship of a God and Goddess.
- Druidry is a religion promoting harmony with nature, and drawing on the practices of the druids.
- Satanism is a broad category of religions that, for example, worship Satan as a deity ( Theistic Satanism) or use "Satan" as a symbol of carnality and earthly values ( LaVeyan Satanism).
Sociological classifications of religious movements suggest that within any given religious group, a community can resemble various types of structures, including "churches", "denominations", "sects", "cults", and "institutions".
Issues in religion
Economics
While there has been much debate about how religion affects the economy of countries, in general there is a negative correlation between religiosity and the wealth of nations. In other words, the richer a nation is, the less religious it tends to be. However, sociologist and political economist Max Weber has argued that Protestant countries are wealthier because of their Protestant work ethic.
Health
Mayo Clinic researchers examined the association between religious involvement and spirituality, and physical health, mental health, health-related quality of life, and other health outcomes. The authors reported that: "Most studies have shown that religious involvement and spirituality are associated with better health outcomes, including greater longevity, coping skills, and health-related quality of life (even during terminal illness) and less anxiety, depression, and suicide." The authors of a subsequent study concluded that the influence of religion on health is "largely beneficial", based on a review of related literature.According to academic James W. Jones, several studies have discovered "positive correlations between religious belief and practice and mental and physical health and longevity."
An analysis of data from the 1998 US General Social Survey, whilst broadly confirming that religious activity was associated with better health and well-being, also suggested that the role of different dimensions of spirituality/religiosity in health is rather more complicated. The results suggested "that it may not be appropriate to generalize findings about the relationship between spirituality/religiosity and health from one form of spirituality/religiosity to another, across denominations, or to assume effects are uniform for men and women.
Violence

Charles Selengut characterizes the phrase "religion and violence" as "jarring", asserting that "religion is thought to be opposed to violence and a force for peace and reconciliation. He acknowledges, however, that "the history and scriptures of the world's religions tell stories of violence and war as they speak of peace and love."
Hector Avalos argues that, because religions claim divine favour for themselves, over and against other groups, this sense of righteousness leads to violence because conflicting claims to superiority, based on unverifiable appeals to God, cannot be adjudicated objectively.
Critics of religion Christopher Hitchens and Richard Dawkins go further and argue that religions do tremendous harm to society by using violence to promote their goals, in ways that are endorsed and exploited by their leaders.
Regina Schwartz argues that all monotheistic religions are inherently violent because of an exclusivism that inevitably fosters violence against those that are considered outsiders. Lawrence Wechsler asserts that Schwartz isn't just arguing that Abrahamic religions have a violent legacy, but that the legacy is actually genocidal in nature.
Byron Bland asserts that one of the most prominent reasons for the "rise of the secular in Western thought" was the reaction against the religious violence of the 16th and 17th centuries. He asserts that "(t)he secular was a way of living with the religious differences that had produced so much horror. Under secularity, political entities have a warrant to make decisions independent from the need to enforce particular versions of religious orthodoxy. Indeed, they may run counter to certain strongly held beliefs if made in the interest of common welfare. Thus, one of the important goals of the secular is to limit violence."
Nonetheless, believers have used similar arguments when responding to atheists in these discussions, pointing to the widespread imprisonment and mass murder of individuals under atheist states in the twentieth century:
And who can deny that Stalin and Mao, not to mention Pol Pot and a host of others, all committed atrocities in the name of a Communist ideology that was explicitly atheistic? Who can dispute that they did their bloody deeds by claiming to be establishing a 'new man' and a religion-free utopia? These were mass murders performed with atheism as a central part of their ideological inspiration, they were not mass murders done by people who simply happened to be atheist.— Dinesh D'Souza
In response to such a line of argument, however, author Sam Harris writes:
The problem with fascism and communism, however, is not that they are too critical of religion; the problem is that they are too much like religions. Such regimes are dogmatic to the core and generally give rise to personality cults that are indistinguishable from cults of religious hero worship. Auschwitz, the gulag and the killing fields were not examples of what happens when human beings reject religious dogma; they are examples of political, racial and nationalistic dogma run amok. There is no society in human history that ever suffered because its people became too reasonable.— Sam Harris
Richard Dawkins has stated that Stalin's atrocities were influenced not by atheism but by dogmatic Marxism, and concludes that while Stalin and Mao happened to be atheists, they did not do their deeds in the name of atheism. On other occasions, Dawkins has replied to the argument that Adolf Hitler and Josef Stalin were antireligious with the response that Hitler and Stalin also grew moustaches, in an effort to show the argument as fallacious. Instead, Dawkins argues in The God Delusion that "What matters is not whether Hitler and Stalin were atheists, but whether atheism systematically influences people to do bad things. There is not the smallest evidence that it does." Dawkins adds that Hitler in fact, repeatedly affirmed a strong belief in Christianity, but that his atrocities were no more attributable to his theism than Stalin's or Mao's were to their atheism. In all three cases, he argues, the perpetrators' level of religiosity was incidental. D'Souza responds that an individual need not explicitly invoke atheism in committing atrocities if it is already implied in his worldview, as is the case in Marxism.
Law
There are laws and statutes that make reference to religion. This has led scholar Winnifred Sullivan to claims that religious freedom is impossible. Others argue that the Western legal principle of separation of church and state tends to engender a new, more inclusive civil religion.
Science
Religious knowledge, according to religious practitioners, may be gained from religious leaders, sacred texts, scriptures, or personal revelation. Some religions view such knowledge as unlimited in scope and suitable to answer any question; others see religious knowledge as playing a more restricted role, often as a complement to knowledge gained through physical observation. Adherents to various religious faiths often maintain that religious knowledge obtained via sacred texts or revelation is absolute and infallible and thereby creates an accompanying religious cosmology, although the proof for such is often tautological and generally limited to the religious texts and revelations that form the foundation of their belief.
In contrast, the scientific method gains knowledge by testing hypotheses to develop theories through elucidation of facts or evaluation by experiments and thus only answers cosmological questions about the universe that can be observed and measured. It develops theories of the world which best fit physically observed evidence. All scientific knowledge is subject to later refinement, or even outright rejection, in the face of additional evidence. Scientific theories that have an overwhelming preponderance of favorable evidence are often treated as de facto verities in general parlance, such as the theories of general relativity and natural selection to explain respectively the mechanisms of gravity and evolution.
Regarding religion and science, Albert Einstein states (1940): "For science can only ascertain what is, but not what should be, and outside of its domain value judgments of all kinds remain necessary. Religion, on the other hand, deals only with evaluations of human thought and action; it cannot justifiably speak of facts and relationships between facts…Now, even though the realms of religion and science in themselves are clearly marked off from each other, nevertheless there exist between the two strong reciprocal relationships and dependencies. Though religion may be that which determine the goals, it has, nevertheless, learned from science, in the broadest sense, what means will contribute to the attainment of the goals it has set up."
Social constructionists
In recent years, some academic writers have described religion according to the theory of social constructionism, which considers how ideas and social phenomena develop in a social context. Among the main proponents of this theory of religion are Timothy Fitzgerald, Daniel Dubuisson and Talal Asad. The social constructionists argue that religion is a modern concept that developed from Christianity and was then applied inappropriately to non-Western cultures.
Dubuisson, a French anthropologist, says that the idea of religion has changed a lot over time and that one cannot fully understand its development by relying on etymology, which "tends to minimize or cancel out the role of history". "What the West and the history of religions in its wake have objectified under the name 'religion'", he says, " is ... something quite unique, which could be appropriate only to itself and its own history." He notes that St. Augustine's definition of religio differed from the way we used the modern word "religion". Dubuisson prefers the term "cosmographic formation" to religion. Dubuisson says that, with the emergence of religion as a category separate from culture and society, there arose religious studies. The initial purpose of religious studies was to demonstrate the superiority of the "living" or "universal" European world view to the "dead" or "ethnic" religions scattered throughout the rest of the world, expanding the teleological project of Schleiermacher and Tiele to a worldwide ideal religiousness. Due to shifting theological currents, this was eventually supplanted by a liberal-ecumenical interest in searching for Western-style universal truths in every cultural tradition. Clifford Geertz's definition of religion as a "cultural system" was proposed in the 20th century and continues to be widely accepted today.
According to Fitzgerald, the history of other cultures' interaction with the religious category is not about a universal constant, but rather concerns a particular idea that first developed in Europe under the influence of Christianity. Fitzgerald argues that from about the 4th century CE Western Europe and the rest of the world diverged. As Christianity became commonplace, the charismatic authority identified by Augustine, a quality we might today call "religiousness", exerted a commanding influence at the local level. This system persisted in the eastern Byzantine Empire following the East-West Schism, but Western Europe regulated unpredictable expressions of charisma through the Roman Catholic Church. As the Church lost its dominance during the Protestant Reformation and Christianity became closely tied to political structures, religion was recast as the basis of national sovereignty, and religious identity gradually became a less universal sense of spirituality and more divisive, locally defined, and tied to nationality. It was at this point that "religion" was dissociated with universal beliefs and moved closer to dogma in both meaning and practice. However there was not yet the idea of dogma as personal choice, only of established churches. With the Enlightenment religion lost its attachment to nationality, says Fitzgerald, but rather than becoming a universal social attitude, it now became a personal feeling or emotion. Friedrich Schleiermacher in the late 18th century defined religion as das schlechthinnige Abhängigkeitsgefühl, commonly translated as "a feeling of absolute dependence". His contemporary Hegel disagreed thoroughly, defining religion as "the Divine Spirit becoming conscious of Himself through the finite spirit."
Asad argues that before the word "religion" came into common usage, Christianity was a disciplina, a "rule" just like that of the Roman Empire. This idea can be found in the writings of St. Augustine (354–430). Christianity was then a power structure opposing and superseding human institutions, a literal Kingdom of Heaven. It was the discipline taught by one's family, school, church, and city authorities, rather than something calling one to self-discipline through symbols.
These ideas are developed by S. N. Balagangadhara. In the Age of Enlightenment, Balagangadhara says that the idea of Christianity as the purest expression of spirituality was supplanted by the concept of "religion" as a worldwide practice. This caused such ideas as religious freedom, a reexamination of classical philosophy as an alternative to Christian thought, and more radically Deism among intellectuals such as Voltaire. Much like Christianity, the idea of "religious freedom" was exported around the world as a civilizing technique, even to regions such as India that had never treated spirituality as a matter of political identity. In Japan, where Buddhism was still seen as a philosophy of natural law, the concept of "religion" and "religious freedom" as separate from other power structures was unnecessary until Christian missionaries demanded free access to conversion, and when Japanese Christians refused to engage in patriotic events.

Other writers
Similar views have been put forward by writers who are not social constructionists. George Lindbeck, a Lutheran and a postliberal theologian, says that religion does not refer to belief in "God" or a transcendent Absolute, but rather to "a kind of cultural and/or linguistic framework or medium that shapes the entirety of life and thought ... it is similar to an idiom that makes possible the description of realities, the formulation of beliefs, and the experiencing of inner attitudes, feelings, and sentiments.” Nicholas de Lange, Professor of Hebrew and Jewish Studies at Cambridge University, says that "The comparative study of religions is an academic discipline which has been developed within Christian theology faculties, and it has a tendency to force widely differing phenomena into a kind of strait-jacket cut to a Christian pattern. The problem is not only that other 'religions' may have little or nothing to say about questions which are of burning importance for Christianity, but that they may not even see themselves as religions in precisely the same way in which Christianity sees itself as a religion."
Animal sacrifice
Animal sacrifice is the ritual killing and offering of an animal to appease or maintain favour with a deity. Such forms of sacrifice are practised within many religions around the world and have appeared historically in almost all cultures.
Related forms of thought
Superstition
Superstition has been described as "the incorrect establishment of cause and effect" or a false conception of causation. Religion is more complex and includes social institutions and morality. But religions may include superstitions or make use of magical thinking. Adherents of one religion sometimes think of other religions as superstition. Some atheists, deists, and skeptics regard religious belief as superstition.
Greek and Roman pagans, who saw their relations with the gods in political and social terms, scorned the man who constantly trembled with fear at the thought of the gods (deisidaimonia), as a slave might fear a cruel and capricious master. The Romans called such fear of the gods superstitio. Early Christianity was outlawed as a superstitio Iudaica, a "Jewish superstition", by Domitian in the 80s AD. In AD 425, when Rome had become Christian, Theodosius II outlawed pagan traditions as superstitious.
The Roman Catholic Church considers superstition to be sinful in the sense that it denotes a lack of trust in the divine providence of God and, as such, is a violation of the first of the Ten Commandments. The Catechism of the Catholic Church states that superstition "in some sense represents a perverse excess of religion" (para. #2110). "Superstition," it says, "is a deviation of religious feeling and of the practices this feeling imposes. It can even affect the worship we offer the true God, e.g., when one attributes an importance in some way magical to certain practices otherwise lawful or necessary. To attribute the efficacy of prayers or of sacramental signs to their mere external performance, apart from the interior dispositions that they demand is to fall into superstition. Cf. Matthew 23:16-22" (para. #2111)
Myth
The word myth has several meanings.
- A traditional story of ostensibly historical events that serves to unfold part of the world view of a people or explain a practice, belief, or natural phenomenon;
- A person or thing having only an imaginary or unverifiable existence; or
- A metaphor for the spiritual potentiality in the human being.
Ancient polytheistic religions, such as those of Greece, Rome, and Scandinavia, are usually categorized under the heading of mythology. Religions of pre-industrial peoples, or cultures in development, are similarly called "myths" in the anthropology of religion. The term "myth" can be used pejoratively by both religious and non-religious people. By defining another person's religious stories and beliefs as mythology, one implies that they are less real or true than one's own religious stories and beliefs. Joseph Campbell remarked, "Mythology is often thought of as other people's religions, and religion can be defined as mis-interpreted mythology."
In sociology, however, the term myth has a non-pejorative meaning. There, myth is defined as a story that is important for the group whether or not it is objectively or provably true. Examples include the death and resurrection of Jesus, which, to Christians, explains the means by which they are freed from sin and is also ostensibly a historical event. But from a mythological outlook, whether or not the event actually occurred is unimportant. Instead, the symbolism of the death of an old "life" and the start of a new "life" is what is most significant. Religious believers may or may not accept such symbolic interpretations.
Secularism and irreligion
The terms "atheist" (lack of belief in any gods) and "agnostic" (belief in the unknowability of the existence of gods), though specifically contrary to theistic (e.g. Christian, Jewish, and Muslim) religious teachings, do not by definition mean the opposite of "religious". There are religions (including Buddhism and Taoism), in fact, that classify some of their followers as agnostic, atheistic, or nontheistic. The true opposite of "religious" is the word "irreligious". Irreligion describes an absence of any religion; antireligion describes an active opposition or aversion toward religions in general.
As religion became a more personal matter in Western culture, discussions of society became more focused on political and scientific meaning, and religious attitudes (dominantly Christian) were increasingly seen as irrelevant for the needs of the European world. On the political side, Ludwig Feuerbach recast Christian beliefs in light of humanism, paving the way for Karl Marx's famous characterization of religion as " the opium of the people". Meanwhile, in the scientific community, T.H. Huxley in 1869 coined the term "agnostic," a term—subsequently adopted by such figures as Robert Ingersoll—that, while directly conflicting with and novel to Christian tradition, is accepted and even embraced in some other religions. Later, Bertrand Russell told the world Why I Am Not a Christian, which influenced several later authors to discuss their breakaway from their own religious uprbringings from Islam to Hinduism.
Parody religions
Parody religions are imitation belief systems that challenge spiritual convictions of others, often through humor, satire, and/or burlesque. Often created to achieve a specific purpose related to another belief system, a parody religion can be a parody of one or more specific systems or even the very concept of religious belief. In some parody religions, emphasis is on making fun and being a convenient excuse for pleasant social interaction among like-minded, e.g. the Church of the SubGenius. Other parody religions target a specific religion, sect, cult, or new religious movement.
One approach to parody religion aims to highlight deficiencies in particular pro-religious arguments — the thinking being that if a given argument can also be used to support a clear parody, then the original argument is clearly flawed. An example of this is the Flying Spaghetti Monster, which parodies the equal time argument employed by intelligent design Creationism.
Several religions that are classified as parody religions have a number of relatively serious followers who embrace the perceived absurdity of these religions as spiritually significant, a decidedly post-modern approach to religion. For instance, in Discordianism, it may be hard to tell if even these "serious" followers are not just taking part in an even bigger joke. This joke, in turn, may be part of a greater path to enlightenment, and so on ad infinitum.
Criticism
Religious criticism has a long history, going back at least as far as the 5th century BCE. During classical times, there were religious critics in ancient Greece, such as Diagoras "the atheist" of Melos, and in the 1st century BCE in Rome, with Titus Lucretius Carus's De Rerum Natura.
During the Middle Ages and continuing into the Renaissance, potential critics of religion were persecuted and largely forced to remain silent. There were notable critics like Giordano Bruno, who was burned at the stake for disagreeing with religious authority.
In the 17th and 18th century with the Enlightenment, thinkers like David Hume and Voltaire criticized religion.
In the 19th century, Charles Darwin and the theory of evolution led to increased skepticism about religion. Thomas Huxley, Jeremy Bentham, Karl Marx, Charles Bradlaugh, Robert Ingersol, and Mark Twain were noted 19th century and early 20th century critics. In the 20th century, Bertrand Russell, Siegmund Freud, and others continued religious criticism.
Sam Harris, Daniel Dennett, Richard Dawkins, Victor J. Stenger, and the late Christopher Hitchens were active critics during the late 20th century and early 21st century.
Critics consider religion to be outdated, harmful to the individual (e.g. brainwashing of children, faith healing, circumcision), harmful to society (e.g. holy wars, terrorism, wasteful distribution of resources), to impede the progress of science, to exert social control, and to encourage immoral acts (e.g. blood sacrifice, discrimination against homosexuals and women). A major criticism of many religions is that they require beliefs that are irrational, unscientific, or unreasonable, because religious beliefs and traditions lack scientific or rational foundations.
Some modern-day critics, such as Bryan Caplan, hold that religion lacks utility in human society; they may regard religion as irrational. Nobel Peace Laureate Shirin Ebadi has spoken out against undemocratic Islamic countries justifying "oppressive acts" in the name of Islam.