Iodine
About this schools Wikipedia selection
This selection is made for schools by a children's charity read more. Before you decide about sponsoring a child, why not learn about different sponsorship charities first?
| Iodine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
53I
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
lustrous metallic gray, violet as a gas |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name, symbol, number | iodine, I, 53 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pronunciation | / ˈ aɪ . ə d aɪ n / EYE-ə-dyn, / ˈ aɪ . ə d ɨ n / EYE-ə-dən, or / ˈ aɪ . ə d iː n / EYE-ə-deen |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Element category | halogen | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group, period, block | 17 (halogens), 5, p | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight | 126.90447 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
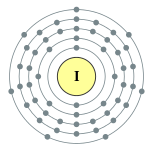
| Electron configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p5 2, 8, 18, 18, 7 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery | Bernard Courtois (1811) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First isolation | Bernard Courtois (1811) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase | solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (near r.t.) | 4.933 g·cm−3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 386.85 K, 113.7 °C, 236.66 °F | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 457.4 K, 184.3 °C, 363.7 °F | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Triple point | 386.65 K (113°C), 12.1 kPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Critical point | 819 K, 11.7 MPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | (I2) 15.52 kJ·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | (I2) 41.57 kJ·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | (I2) 54.44 J·mol−1·K−1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure (rhombic) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | 7, 5, 3, 1, -1 (strongly acidic oxide) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | 2.66 (Pauling scale) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies | 1st: 1008.4 kJ·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2nd: 1845.9 kJ·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3rd: 3180 kJ·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius | 140 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 139±3 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 198 pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellanea | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | orthorhombic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical resistivity | (0 °C) 1.3×107Ω·m | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 0.449 W·m−1·K−1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bulk modulus | 7.7 GPa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS registry number | 7553-56-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Most stable isotopes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main article: Isotopes of iodine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Iodine is a chemical element with symbol I and atomic number 53. The name is from Greek ἰοειδής ioeidēs, meaning violet or purple, due to the colour of elemental iodine vapor.
Iodine and its compounds are primarily used in nutrition, and industrially in the production of acetic acid and certain polymers. Iodine's relatively high atomic number, low toxicity, and ease of attachment to organic compounds have made it a part of many X-ray contrast materials in modern medicine. Iodine has only one stable isotope. A number of iodine radioisotopes are also used in medical applications.
Iodine is found on Earth mainly as the highly water-soluble iodide ion, I−, which concentrates it in oceans and brine pools. Like the other halogens, free iodine occurs mainly as a diatomic molecule I2, and then only momentarily after being oxidized from iodide by an oxidant like free oxygen. In the universe and on Earth, iodine's high atomic number makes it a relatively rare element. However, its presence in ocean water has given it a role in biology. It is the heaviest essential element utilized widely by life in biological functions (only tungsten, employed in enzymes by a few species of bacteria, is heavier). Iodine's rarity in many soils, due to initial low abundance as a crust-element, and also leaching of soluble iodide by rainwater, has led to many deficiency problems in land animals and inland human populations. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities.
Iodine is required by higher animals, which use it to synthesize thyroid hormones, which contain the element. Because of this function, radioisotopes of iodine are concentrated in the thyroid gland along with nonradioactive iodine. If inhaled, the radioisotope iodine-131, which has a high fission product yield, concentrates in the thyroid, but is easily remedied with potassium iodide treatment.
Characteristics
Iodine under standard conditions is a bluish-black solid. It can be seen apparently sublimating at standard temperatures into a violet-pink gas that has an irritating odour. This halogen forms compounds with many elements, but is less reactive than the other members of its Group VII (halogens) and has some metallic light reflectance.
Elemental iodine dissolves easily in most organic solvents such as hexane or chloroform owing to its lack of polarity, but is only slightly soluble in water. However, the solubility of elemental iodine in water can be increased by the addition of potassium iodide. The molecular iodine reacts reversibly with the negative ion, generating the triiodide anion I3− in equilibrium, which is soluble in water. This is also the formulation of some types of medicinal (antiseptic) iodine, although tincture of iodine classically dissolves the element in aqueous ethanol.
Iodine melts at the relatively low temperature of 113.7 °C, although the liquid is often obscured by a dense violet vapor of gaseous iodine.
Iodine in the gas phase is violet in colour, this is due to certain wavelengths of visible light absorbed when an electronic transition from the highest occupied π* MO to the lowest unoccupied σ* MO in the molecule occurs. When iodine is dissolved in polar solvents which are strong donor solvents such as ketones, ethers, pyridine, the formation of charge-transfer complex leads to modification of the energy gap between the two molecular orbitals, thus different wavelengths were absorbed and iodine has different colour in solvents with different polarity.
Solutions of iodine in strong donor solvents such as acetone, tetrahydrofuran, pyridine appears brown or yellow (λmax = 460-480 nm), while in solvents of weaker donors such as dichloromethane it appears crimson red, in aromatic hydrocarbons such as benzene and toluene it appears pink or reddish-brown. In non-polar solvents such as hexane, no charge-transfer complexes is formed, and the solution appears violet (λmax = 520-540 nm) since the energy gap in I2 in non-polar solvents is essentially the same as that in the gas phase. When a brown solution of iodine in a strong donor solvent is heated, a colour transition from brown to violet is observed as the weakly bonded charge-transfer complex dissociates into to free solvent and iodine molecules.
Charge-transfer complexes can also be formed between iodine and a metal ion, in which electrons in the filled π* orbitals of iodine molecules were donated to the empty, low-lying 5s and 5d orbitals, meanwhile back donation from the metal occurs, which weakens and lengthens the I—I bond. An example is [AgI2] [SbF6] where a polymeric chain of the charge-transfer complex [(AgI2)n]n+ exists in the compound.
Occurrence
Iodine is rare in the solar system and Earth's crust (47–60th in abundance); however, iodide salts are often very soluble in water. Iodine occurs in slightly greater concentrations in seawater than in rocks, 0.05 vs. 0.04 ppm. Minerals containing iodine include caliche, found in Chile. The brown algae Laminaria and Fucus found in temperate zones of the Northern Hemisphere contain 0.028–0.454 dry weight percent of iodine. Aside from tungsten, iodine is the heaviest element to be essential in living organisms. About 19,000 tonnes are produced annually from natural sources.
Organoiodine compounds are produced by marine life forms, the most notable being iodomethane (commonly called methyl iodide). About 214 kilotonnes/year of iodomethane is produced by the marine environment, by microbial activity in rice paddies and by the burning of biological material. The volatile iodomethane is broken up in the atmosphere as part of a global iodine cycle.
Structure and bonding
Iodine normally exists as a diatomic molecule with an I-I bond length of 270 pm, one of the longest single bonds known. The I2 molecules tend to interact via the weak van der Waals forces called the London dispersion forces, and this interaction is responsible for the higher melting point compared to more compact halogens, which are also diatomic. Since the atomic size of iodine is larger, its melting point is higher. The solid crystallizes as orthorhombic crystals. The crystal motif in the Hermann–Mauguin notation is Cmca (No 64), Pearson symbol oS8. The I-I bond is relatively weak, with a bond dissociation energy of 36 kcal/mol, and most bonds to iodine are weaker than for the lighter halides. One consequence of this weak bonding is the relatively high tendency of I2 molecules to dissociate into atomic iodine.
Production
Of the several places in which iodine occurs in nature, only two sources are useful commercially: the caliche, found in Chile, and the iodine-containing brines of gas and oil fields, especially in Japan and the United States. The caliche contains sodium nitrate, which is the main product of the mining activities, and small amounts of sodium iodate and sodium iodide. In the extraction of sodium nitrate, the sodium iodate and sodium iodide are extracted. The high concentration of iodine in the caliche and the extensive mining made Chile the largest producer of iodine in 2007.
Most other producers use natural occurring brine for the production of iodine. The Japanese Minami Kanto gas field east of Tokyo and the American Anadarko Basin gas field in northwest Oklahoma are the two largest sources for iodine from brine. The brine has a temperature of over 60°C owing to the depth of the source. The brine is first purified and acidified using sulfuric acid, then the iodide present is oxidized to iodine with chlorine. An iodine solution is produced, but is dilute and must be concentrated. Air is blown into the solution, causing the iodine to evaporate, then it is passed into an absorbing tower containing acid where sulfur dioxide is added to reduce the iodine. The hydrogen iodide (HI) is reacted with chlorine to precipitate the iodine. After filtering and purification the iodine is packed.
- 2 HI + Cl2 → I2↑ + 2 HCl
- I2 + 2 H2O + SO2 → 2 HI + H2SO4
- 2 HI + Cl2 → I2↓ + 2 HCl
The production of iodine from seawater via electrolysis is not used owing to the sufficient abundance of iodine-rich brine. Another source of iodine is kelp, used in the 18th and 19th centuries, but it is no longer economically viable.
Commercial samples often contain high concentrations of impurities, which can be removed by sublimation. The element may also be prepared in an ultra-pure form through the reaction of potassium iodide with copper(II) sulfate, which gives copper(II) iodide initially. That decomposes spontaneously to copper(I) iodide and iodine:
- Cu2+ + 2 I– → CuI2
- 2 CuI2 → 2 CuI + I2
There are also other methods of isolating this element in the laboratory, for example, the method used to isolate other halogens: oxidation of the iodide in hydrogen iodide (often made in situ with an iodide and sulfuric acid) by manganese dioxide (see below in Descriptive chemistry).
Isotopes and their applications
Of the 37 known (characterized) isotopes of iodine, only one, 127I, is stable.
The longest-lived radioisotope, 129I, has a half-life of 15.7 million years. This is long enough to make it a permanent fixture of the environment on human time scales, but far too short for it to exist as a primordial isotope today. Instead, iodine-129 is an extinct radionuclide, and its presence in the early solar system is inferred from the observation of an excess of its daughter xenon-129. This nuclide is also newly made by cosmic rays and as a byproduct of human nuclear fission, which it is used to monitor as a very long-lived environmental contaminant.
The next-longest-lived radioisotope, iodine-125, has a half-life of 59 days. It is used as a convenient gamma-emitting tag for proteins in biological assays, and a few nuclear medicine imaging tests where a longer half-life is required. It is also commonly used in brachytherapy implanted capsules, which kill tumors by local short-range gamma radiation (but where the isotope is never released into the body).
Iodine-123 (half-life 13 hours) is the isotope of choice for nuclear medicine imaging of the thyroid gland, which naturally accumulates all iodine isotopes.
Iodine-131 (half-life 8 days) is a beta-emitting isotope, which is a common nuclear fission product. It is preferably administered to humans only in very high doses which destroy all tissues that accumulate it (usually the thyroid), which in turn prevents these tissues from developing cancer from a lower dose (paradoxically, a high dose of this isotope appears safer for the thyroid than a low dose). Like other radioiodines, I-131 accumulates in the thyroid gland, but unlike the others, in small amounts it is highly carcinogenic there, it seems, owing to the high local cell mutation due to damage from beta decay. Because of this tendency of 131I to cause high damage to cells that accumulate it and other cells near them (0.6 to 2 mm away, the range of the beta rays), it is the only iodine radioisotope used as direct therapy, to kill tissues such as cancers that take up artificially iodinated molecules (example, the compound iobenguane, also known as MIBG). For the same reason, only the iodine isotope I-131 is used to treat Grave's disease and those types of thyroid cancers (sometimes in metastatic form) where the tissue that requires destruction, still functions to naturally accumulate iodide.
Nonradioactive ordinary potassium iodide (iodine-127), in a number of convenient forms (tablets or solution) may be used to saturate the thyroid gland's ability to take up further iodine, and thus protect against accidental contamination from iodine-131 generated by nuclear fission accidents, such as the Chernobyl disaster and more recently the Fukushima I nuclear accidents, as well as from contamination from this isotope in nuclear fallout from nuclear weapons.
History
Iodine was discovered by French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811. He was born to a manufacturer of saltpeter (a vital part of gunpowder). At the time of the Napoleonic Wars, France was at war and saltpeter was in great demand. Saltpeter produced from French niter beds required sodium carbonate, which could be isolated from seaweed collected on the coasts of Normandy and Brittany. To isolate the sodium carbonate, seaweed was burned and the ash washed with water. The remaining waste was destroyed by adding sulfuric acid. Courtois once added excessive sulfuric acid and a cloud of purple vapor rose. He noted that the vapor crystallized on cold surfaces, making dark crystals. Courtois suspected that this was a new element but lacked funding to pursue it further.
Courtois gave samples to his friends, Charles Bernard Desormes (1777–1862) and Nicolas Clément (1779–1841), to continue research. He also gave some of the substance to chemist Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac (1778–1850), and to physicist André-Marie Ampère (1775–1836). On 29 November 1813, Dersormes and Clément made public Courtois's discovery. They described the substance to a meeting of the Imperial Institute of France. On December 6, Gay-Lussac announced that the new substance was either an element or a compound of oxygen. It was Gay-Lussac who suggested the name "iode", from the Greek word ιώδες (iodes) for violet (because of the colour of iodine vapor). Ampère had given some of his sample to Humphry Davy (1778–1829). Davy did some experiments on the substance and noted its similarity to chlorine. Davy sent a letter dated December 10 to the Royal Society of London stating that he had identified a new element. Arguments erupted between Davy and Gay-Lussac over who identified iodine first, but both scientists acknowledged Courtois as the first to isolate the element.
Applications
Human food additive
This very important application is discussed in the sections at the end of this article, which treat iodine in biology.
Animal feed
The production of ethylenediammonium diiodide (EDDI) consumes a large fraction of available iodine. EDDI is provided to livestock as a nutritional supplement.
Catalysis
The major application of iodine is as a co-catalyst for the production of acetic acid by the Monsanto and Cativa processes. In these technologies, which support the world's demand for acetic acid, hydroiodic acid converts the methanol feedstock into methyl iodide, which undergoes carbonylation. Hydrolysis of the resulting acetyl iodide regenerates hydroiodic acid and gives acetic acid.
Disinfectant and water treatment
Elemental iodine is used as a disinfectant in various forms. The iodine exists as the element, or as the water-soluble triiodide anion I3- generated in situ by adding iodide to poorly water-soluble elemental iodine (the reverse chemical reaction makes some free elemental iodine available for antisepsis). In alternative fashion, iodine may come from iodophors, which contain iodine complexed with a solubilizing agent (iodide ion may be thought of loosely as the iodophor in triiodide water solutions). Examples of such preparations include:
- Tincture of iodine: iodine in ethanol, or iodine and sodium iodide in a mixture of ethanol and water.
- Lugol's iodine: iodine and iodide in water alone, forming mostly triiodide. Unlike tincture of iodine, Lugol's has a minimized amount of the free iodine (I2) component.
- Povidone iodine (an iodophor).
Medical and radiological use
Potassium iodide has been used as an expectorant, although this use is increasingly uncommon. In medicine, potassium iodide is usually used to treat acute thyrotoxicosis, usually as a saturated solution of potassium iodide called SSKI. It is also used to block uptake of iodine-131 in the thyroid gland (see isotopes section above), when this isotope is used as part of radiopharmaceuticals (such as iobenguane) that are not targeted to the thyroid or thyroid-type tissues.
Iodine-131 (usually in the chemical form of iodide) is a component of nuclear fallout and a particularly dangerous one owing to the thyroid gland's propensity to concentrate ingested iodine, where it is kept for periods longer than this isotope's radiological half-life of eight days. For this reason, if people are expected to be exposed to a significant amount of environmental radioactive iodine (iodine-131 in fallout), they may be instructed to take non-radioactive potassium iodide tablets. The typical adult dose is one 130 mg tablet per 24 hours, supplying 100 mg (100,000 micrograms) iodine, as iodide ion. (Typical daily dose of iodine to maintain normal health is of order 100 micrograms; see "Dietary Intake" below.) By ingesting this large amount of non-radioactive iodine, radioactive iodine uptake by the thyroid gland is minimized. See the article on potassium iodide for more on this topic.
Radiocontrast agent
Iodine, as a physically dense element with high electron density and high atomic number, is quite radio-opaque (i.e., it absorbs X-rays well). This property can be fully exploited by filtering imaging X-rays so that they are more energetic than iodine's "K-edge" at 33.3 keV, or the energy where the iodine begins to absorb X-rays strongly due to the photoelectric effect from electrons in its K shell. Organic compounds of a certain type (typically iodine-substituted benzene derivatives) are thus used in medicine as X-ray radiocontrast agents for intravenous injection. This is often in conjunction with advanced X-ray techniques such as angiography and CT scanning. At present, all water-soluble radiocontrast agents rely on iodine.
Other uses
Inorganic iodides find specialized uses. Hafnium, zirconium, titanium are purified by the van Arkel Process, which involves the reversible formation of the tetraiodides of these elements. Silver iodide is a major ingredient to traditional photographic film. Thousands of kilograms of silver iodide are consumed annually for cloud seeding.
The organoiodine compound erythrosine is an important food coloring agent. Perfluoroalkyl iodides are precursors to important surfactants, such as perfluorooctanesulfonic acid.
Iodine chemistry
Iodine adopts a variety of oxidation states, commonly ranging from (formally) I(VII) to I(-I), and including the intermediate states of I(V), I(III) and I(I). Practically, only the -1 oxidation state is of significance, being the form found in iodide salts and organoiodine compounds. Iodine is a Lewis acid. With electron donors such as triphenylphosphine and pyridine it forms a charge-transfer complex. With the iodide anion it forms the triiodide ion. Iodine and the iodide ion form a redox couple. I2 is easily reduced and I- is easily oxidized.
Solubility
Being a nonpolar molecule, iodine is highly soluble in nonpolar organic solvents, including ethanol (20.5 g/100 ml at 15 °C, 21.43 g/100 ml at 25 °C), diethyl ether (20.6 g/100 ml at 17 °C, 25.20 g/100 ml at 25 °C), chloroform, acetic acid, glycerol, benzene (14.09 g/100 ml at 25 °C), carbon tetrachloride (2.603 g/100 ml at 35 °C), and carbon disulfide (16.47 g/100 ml at 25 °C). Elemental iodine is poorly soluble in water, with one gram dissolving in 3450 ml at 20 °C and 1280 ml at 50 °C, although it is a lot more soluble in iodide solution as it forms polyiodide ions. Aqueous and ethanol solutions are brown reflecting the role of these solvents as Lewis bases. Solutions in chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, and carbon disulfide are violet, the colour of iodine vapor.
Redox reactions
In everyday life, iodides are slowly oxidized by atmospheric oxygen in the atmosphere to give free iodine. Evidence for this conversion is the yellow tint of certain aged samples of iodide salts and some organoiodine compounds. The oxidation of iodide to iodine in air is also responsible for the slow loss of iodide content in iodized salt if exposed to air. Some salts use iodate to prevent the loss of iodine.
Iodine is easily reduced. Most common is the interconversion of I- and I2. Molecular iodine can be prepared by oxidizing iodides with chlorine:
- 2 I− + Cl2 → I2 + 2 Cl−
or with manganese dioxide in acid solution:
- 2 I− + 4 H+ + MnO2 → I2 + 2 H2O + Mn2+
Iodine is reduced to hydroiodic acid by hydrogen sulfide and hydrazine:
- 8 I2 + 8 H2S → 16 HI + S8
- 2 I2 + N2H4 → 4 HI + N2
When dissolved in fuming sulfuric acid (65% oleum), iodine forms an intense blue solution. The blue colour is due to I+
2 cation, the result of iodine being oxidized by SO3:
- 2 I2 + 2 SO3 + H2SO4 → 2 I+
2 + SO2 + 2 HSO−
4
The I+
2 cation is also formed in the oxidation of iodine by SbF5 or TaF5. The resulting I+
2Sb
2F−
11 or I+
2Ta
2F−
11 can be isolated as deep blue crystals. The solutions of these salts turn red when cooled below −60°C, owing to the formation of the I2+
4 cation:
- 2 I+
2 I2+
I2+
4
Under slightly more alkaline conditions, I2+
4 disproportionates into I+
3 and an iodine(III) compound. Excess iodine can then react with I+
3 to form I+
5 (green) and I3+
15 (black).
Oxides of iodine
The best-known oxides are the anions, IO−
3 and IO−
4, but several other oxides are known, such as the strong oxidant iodine pentoxide.
By contrast with chlorine, the formation of the hypohalite ion (IO–) in neutral aqueous solutions of iodine is negligible.
- I2 + H2O
 H+ + I− + HIO (K = 2.0×10−13) In basic solutions (such as aqueous sodium hydroxide), iodine converts in a two stage reaction to iodide and iodate:
H+ + I− + HIO (K = 2.0×10−13) In basic solutions (such as aqueous sodium hydroxide), iodine converts in a two stage reaction to iodide and iodate:
-
I2 + 2 OH− → I− + IO− + H2O (K = 30) 3 IO− → 2 I− + IO−
3(K = 1020)
Organic derivatives of hypoiodate ( 2-Iodoxybenzoic acid, and Dess-Martin periodinane) are used in organic chemistry.
Iodic acid (HIO3), periodic acid (HIO4) and their salts are strong oxidizers and are of some use in organic synthesis. Iodine is oxidized to iodate by nitric acid as well as by chlorates:
- I2 + 10 HNO3 → 2 HIO3 + 10 NO2 + 4 H2O
- I2 + 2 ClO−
3 → 2 IO−
3 + Cl2
Inorganic iodine compounds
Iodine forms compounds with all the elements except for the noble gases. From the perspective of commercial applications, an important compound is hydroiodic acid, used as a co-catalyst in the Cativa process for the production of acetic acid. Titanium and aluminium iodides are used in the production of butadiene, a precursor to rubber tires.
Alkali metal salts are common colourless solids that are highly soluble in water. Potassium iodide is a convenient source of the iodide anion; it is easier to handle than sodium iodide because it is not hygroscopic. Both salts are mainly used in the production of iodized salt. Sodium iodide is especially useful in the Finkelstein reaction, because it is soluble in acetone, whereas potassium iodide is less so. In this reaction, an alkyl chloride is converted to an alkyl iodide. This relies on the insolubility of sodium chloride in acetone to drive the reaction:
- R-Cl (acetone) + NaI (acetone) → R-I (acetone) + NaCl (s)
Despite having the lowest electronegativity of the common halogens, iodine reacts violently with some metals, such as aluminium:
- 3 I2 + 2 Al → 2 AlI3
This reaction produces 314 kJ per mole of aluminium, comparable to thermite's 425 kJ. Yet the reaction initiates spontaneously, and if unconfined, causes a cloud of gaseous iodine due to the high temperature.
Interhalogen compounds
Interhalogen compounds are well known; examples include iodine monochloride and trichloride; iodine pentafluoride and heptafluoride.
Organic compounds
Many organoiodine compounds exist; the simplest is iodomethane, approved as a soil fumigant. Iodinated organic compounds are used as synthetic reagents.
Organic synthesis
Organoiodine compounds can be made in many ways. For example, methyl iodide can be prepared from methanol, red phosphorus, and iodine. The iodinating reagent is phosphorus triiodide that is formed in situ:
- 3 CH3OH + PI3 → 3 CH3I + H3PO3
The iodoform test uses an alkaline solution of iodine to react with methyl ketones to give the labile triiodomethide leaving group, forming iodoform, which precipitates.
Aryl and alkyl iodides both form Grignard reagents. Iodine is sometimes used to activate magnesium when preparing Grignard reagents. Alkyl iodides such as iodomethane are good alkylating agents. Some drawbacks to use of organoiodine compounds in chemical synthesis are:
- iodine compounds are more expensive than the corresponding bromides and chlorides, in that order
- iodides are much stronger alkylating agents, and so are more toxic (e.g., methyl iodide is very toxic (T+).
- low-molecular-weight iodides tend to have a much higher equivalent weight, compared to other alkylating agents (e.g., methyl iodide versus dimethyl carbonate), owing to the atomic mass of iodine.
Analytical chemistry and bioanalysis
Iodine is useful in analytical chemistry because of its reactions with alkenes, starch and oxidizing and reducing agents. The highly colored species involved in these reactions make it easy to detect the endpoints in many analytical determinations. Iodine is a common general stain used in thin-layer chromatography. Iodine forms an intense blue complex with the glucose polymers starch and glycogen. Several analytical methods rely on this property:
- Iodometry. The concentration of an oxidant can be determined by adding it to an excess of iodide, to destroy elemental iodine/triiodide as a result of oxidation by the oxidant. A starch indicator is then used as the indicator close to the end-point, in order to increase the visual contrast (dark blue becomes colorless, instead of the yellow of dilute triiodide becoming colorless).
- An Iodine test may be used to test a sample substance for the presence of starch. The Iodine clock reaction is an extension of the techniques in iodometry.
- Iodine solutions are used in counterfeit banknote detection pens; the premise being that counterfeit banknotes made using commercially available paper contain starch.
- Starch-iodide paper are used to test for the presence of oxidants such as peroxides. The oxidants convert iodide to iodine, which shows up as blue. A solution of starch and iodide can perform the same function.
- During colposcopy, Lugol's iodine is applied to the vagina and cervix. Normal vaginal tissue stains brown owing to its high glycogen content (a colour-reaction similar to that with starch), while abnormal tissue suspicious for cancer does not stain, and thus appears pale compared to the surrounding tissue. Biopsy of suspicious tissue can then be performed. This is called a Schiller's Test.
Iodine value or iodine number is used to indicate the number of carbon-carbon double bonds in vegetable oils and fatty acids.
Clandestine synthetic chemical use
In the United States, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) regards iodine and compounds containing iodine (ionic iodides, iodoform, ethyl iodide, and so on) as reagents useful for the clandestine manufacture of methamphetamine.
Biological role
Iodine is an essential trace element for life, the heaviest element commonly needed by living organisms. Only tungsten, a component of a few bacterial enzymes, has a higher atomic number and atomic weight.
Iodine's main role in animal biology is as a constituent of the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These are made from addition condensation products of the amino acid tyrosine, and are stored prior to release in an iodine-containing protein called thyroglobulin. T4 and T3 contain four and three atoms of iodine per molecule, respectively. The thyroid gland actively absorbs iodide from the blood to make and release these hormones into the blood, actions that are regulated by a second hormone TSH from the pituitary. Thyroid hormones are phylogenetically very old molecules that are synthesized by most multicellular organisms, and that even have some effect on unicellular organisms.
Thyroid hormones play a basic role in biology, acting on gene transcription to regulate the basal metabolic rate. The total deficiency of thyroid hormones can reduce basal metabolic rate up to 50%, while in excessive production of thyroid hormones the basal metabolic rate can be increased by 100%. T4 acts largely as a precursor to T3, which is (with minor exceptions) the biologically active hormone. In amphibian metamorphosis iodine and thyroid hormones exert a well-studied experimental model of apoptosis on the cells of gills, tail, and fins of tadpoles.
Iodine has a nutritional relationship with selenium. A family of selenium-dependent enzymes called deiodinases converts T4 to T3 (the active hormone) by removing an iodine atom from the outer tyrosine ring. These enzymes also convert T4 to reverse T3 (rT3) by removing an inner ring iodine atom, and convert T3 to 3,3'-diiodothyronine (T2) also by removing an inner ring atom. Both of the latter are inactivated hormones that are ready for disposal and have, in essence, no biological effects. A family of non-selenium-dependent enzymes then further deiodinates the products of these reactions.
Iodine accounts for 65% of the molecular weight of T4 and 59% of the T3. Fifteen to 20 mg of iodine is concentrated in thyroid tissue and hormones, but 70% of the body's iodine is distributed in other tissues, including mammary glands, eyes, gastric mucosa, arterial walls, the cervix, and salivary glands. In the cells of these tissues, iodide enters directly by sodium-iodide symporter (NIS). Its role in mammary tissue is related to fetal and neonatal development, but its role in the other tissues is unknown.
Dietary intake
The daily Dietary Reference Intake recommended by the United States Institute of Medicine is between 110 and 130 µg for infants up to 12 months, 90 µg for children up to eight years, 130 µg for children up to 13 years, 150 µg for adults, 220 µg for pregnant women and 290 µg for lactating mothers. The Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) for adults is 1,100 μg/day (1.1 mg/day). The tolerable upper limit was assessed by analyzing the effect of supplementation on thyroid-stimulating hormone.
The thyroid gland needs no more than 70 micrograms/day to synthesize the requisite daily amounts of T4 and T3. The higher recommended daily allowance levels of iodine seem necessary for optimal function of a number of body systems, including lactating breast, gastric mucosa, salivary glands, oral mucosa, arterial walls
Natural sources of iodine include sea life, such as kelp and certain seafood, as well as plants grown on iodine-rich soil. Iodized salt is fortified with iodine.
As of 2000, the median intake of iodine from food in the United States was 240 to 300 μg/day for men and 190 to 210 μg/day for women. In Japan, consumption is much higher, ranging between 5,280 μg/day to 13,800 μg/day, this owing to the frequent consumption of seaweed or kombu kelp.
After iodine fortification programs (e.g., iodized salt) have been implemented, some cases of iodine-induced hyperthyroidism have been observed (so-called Jod-Basedow phenomenon). The condition seems to occur mainly in people over forty, and the risk appears higher when iodine deficiency is severe and the initial rise in iodine intake is high.
Information processing, fine motor skills, and visual problem solving are improved by iodine repletion in moderately iodine-deficient children.
Deficiency
In an estimated two-thirds of households on Earth, table salt is iodized. However, this still leaves an estimated two billion people iodine-deficient. Iodine is required for the essential thyroxin hormones produced by and concentrated in the thyroid gland.
In areas where there is little iodine in the diet, typically remote inland areas and semi-arid equatorial climates where no marine foods are eaten, iodine deficiency gives rise to hypothyroidism, symptoms of which are extreme fatigue, goitre, mental slowing, depression, weight gain, and low basal body temperatures. Iodine deficiency is the leading cause of preventable mental retardation, a result that occurs primarily when babies or small children are rendered hypothyroidic by a lack of the element. The addition of iodine to table salt has largely eliminated this problem in the wealthier nations, but, as of March 2006, iodine deficiency remained a serious public health problem in the developing world. Iodine deficiency is also a problem in certain areas of Europe.
Other possible health effects being investigated as being related to deficiency include:
- Breast cancer. The breast strongly and actively concentrates iodine into breast-milk for the benefit of the developing infant, and may develop a goiter-like hyperplasia, sometimes manifesting as fibrocystic breast disease, when iodine levels are low.
- Stomach cancer. Some researchers have found an epidemiologic correlation between iodine deficiency, iodine-deficient goitre and gastric cancer. A decrease of the incidence of death rate from stomach cancer after implementation of the effective iodine-prophylaxis has been reported also.
Precautions and toxicity of elemental iodine
Elemental iodine (I2) is toxic if taken orally. The lethal dose for an adult human is 30 mg/kg, which is about 2.1-2.4 grams (even if experiments on rats demonstrated that these animals could survive after eating a 14000 mg/kg dose). Excess iodine can be more cytotoxic in the presence of selenium deficiency. Iodine supplementation in selenium-deficient populations is, in theory, problematic, partly for this reason. Its toxicity derives from its oxidizing properties, which make it able to denaturate proteins (and so also enzymes).
Elemental iodine is an oxidizing irritant and direct contact with skin can cause lesions, so iodine crystals should be handled with care. Solutions with high elemental iodine concentration such as tincture of iodine and Lugol's solution are capable of causing tissue damage if their use for cleaning and antiseptics is prolonged.
Iodine sensitivity
Some people develop a sensitivity to iodine. Application of tincture of iodine can cause a rash. Some cases of reaction to Povidone-iodine (Betadine) resulted in chemical burns. Medical use of iodine (i.e. as a contrast agent, see above) can cause anaphylactic shock in highly iodine-sensitive patients. Some cases of sensitivity to iodine can be formally classified as iodine allergies. Iodine sensitivity is rare but has a considerable effect given the extremely widespread use of iodine-based contrast media.